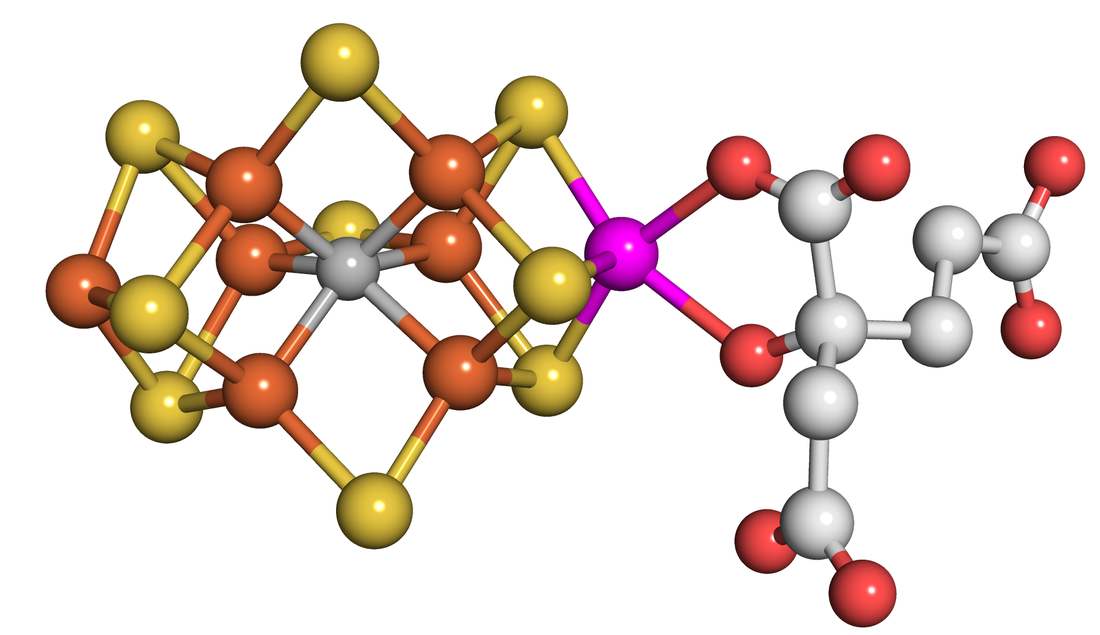
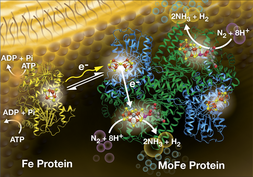
Nitrogenase: Reduction of N2Research in the group is focused on gaining molecular level insights into the reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia, a reaction central to life on Earth. We focus on the microbial enzyme nitrogenase, the bacterial enzyme that catalyzes all biological dinitrogen reduction under green conditions.
|
Molecular Details of the Nitrogenase Mechanism A wide range of approaches are used in our studies, with the common goal of understanding how this catalyst functions both inside microbes and when in a purified state. Molecular level insights include an understanding of how N2 binds and is reduced at the active site and how the active site metal cluster controls competing reduction reactions. Outcomes from these studies are expected to inform the design of next generation catalysts for the production of green ammonia.
|
News
|
|
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
Utah State University 0300 Old Main Hill Logan, UT 84322 Ph. +1.435.797.3964 email. [email protected] |